The first consumer of water jets pump was James Thompson back in 1852. In 1870, J. M. Rankin introduced the theory of jet pump operation, afterward, a number of papers have been published to develop the technology. The work of Gasoline and O’Brien in 1933 is considered to be the standard reference work. It has been based on both theoretical and experimental results. Since that time, developments in the technology have continued to the point that today jet pumps have high operational flexibility.
What is Hydraulic Lift?
As a general description, Hydraulic Lift (Jet Pumps) represents pumping power fluid at high pressure and rate from surface to activate/drive a downhole pump. Power Fluid can be water or oil.
With Jet Pump applications the completion needs to have minimum 3 flowing conduits:
- A conduit for power fluid injection (inside of the tubing in case of standard flow, and in the annular space in case of reverse flow).
- For reservoir fluid flow (below the JP & packer).
- And a conduit for commingled fluid flow to the surface.
Jet Pump working principle:
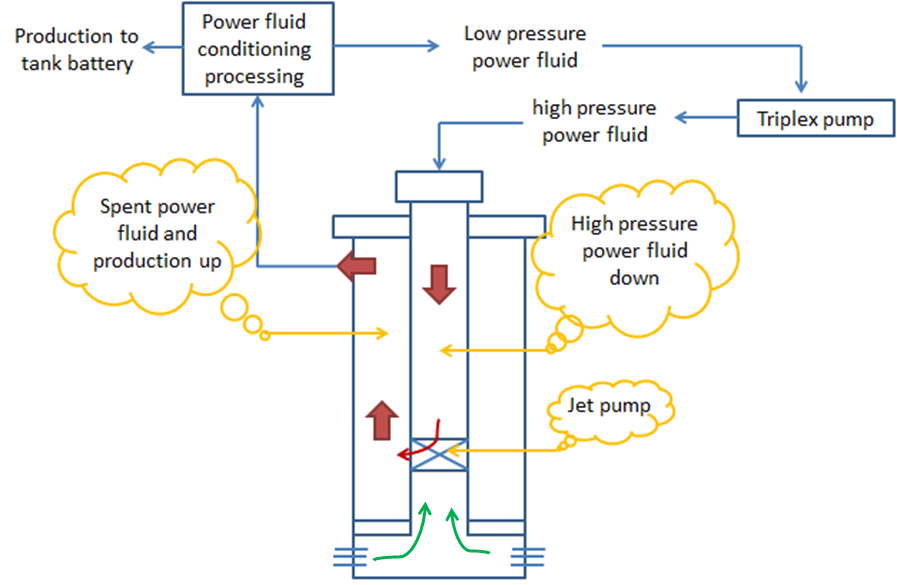
The jet pump artificial lift system is composed of two principal parts: the surface pumping equipment and the downhole jet pump. In the surface, the reciprocating pump transfers energy to the fluid increases its pressure, drove through surface piping, production tubing (or annular space) until the jet pump, placed on the bottom.
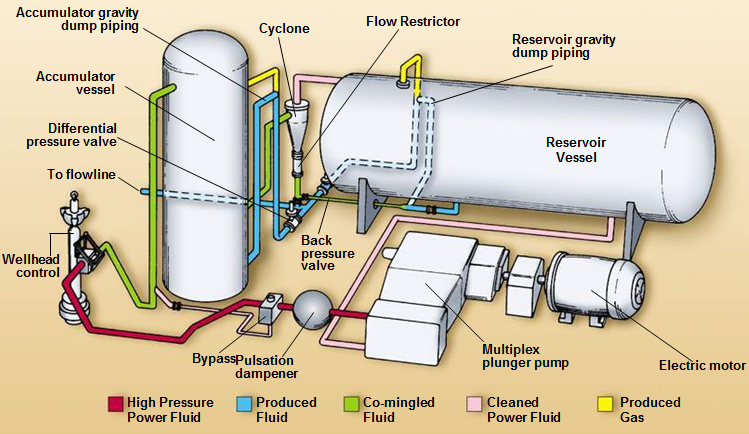
Surface Equipment consists of the power unit (high-pressure pump with accessories, motor, gear reducer, controller), power fluid conditioning unit (VCU) and high-pressure lines. The following figure gives an example of a typical jet pump surface equipment configuration:
When the power fluid travels at high pressure through the smaller area of the jet pump, known as “nozzle“, the Venturi effect occurs increasing the speed and reducing the pressure. This generates the suction of reservoir fluids in the space between the nozzle and the throat.
When the power fluid gets into the mixing tube the flow area increases, reversing the energy transformation, reducing speed, and increasing the pressure. This allows the reservoir fluids to be lifted to the surface through the annular space. Downhole jet pump compounds and their working principle are detailed in the article “How Does Jet Pump Work?”.
The nozzle and throat are the key components of a jet pump. The ratio of the areas of these two parts is known as the area ratio of the pump and it determines the performance characteristics of the pump. Pumps with the same area ratio have the same performance and efficiency curves
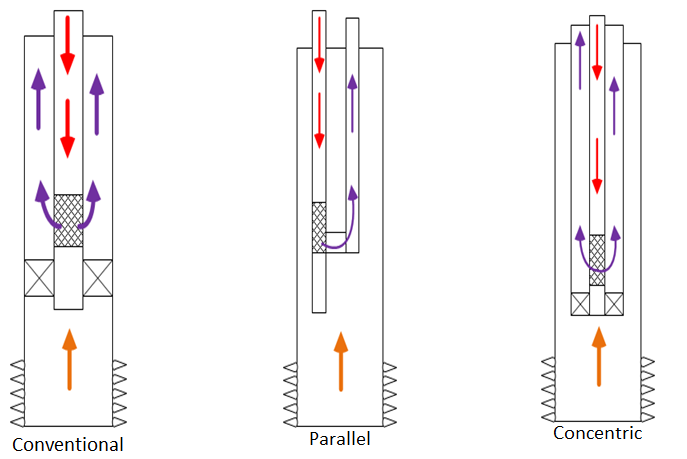
Completion Types:
There are three typical completion types for wells equipped with downhole jet pump: Conventional, Parallel and Concentric.