As shown in the figure below, the main cable consists of three conductor wires extending from the top of the motor flat lead extension to the wellhead banded to the production tubing. The ESP cable carries current (amperage) from the motor controller at the surface down to the motor.
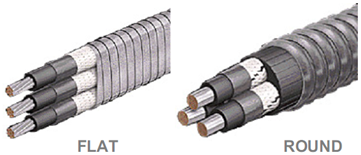
Round and flat configurations are available in various materials and sizes. Common volatage ratings for submersible pump cable are 3, 4 and 5 KV.
Power cable compounds:
The major components of a power cable are:
|
 |
Cable conductor: The AC current is carried from the surface to the motor using cable conductor. It is generally made of copper but some aluminum cable conductors exist. For ESP applications, four sizes of conductors have been standardized: #1, #2, #4 and #6 AWG. The conductors may be solid, stranded, or compact stranded. Refer to the article ” Cable conductors ” for more details related to conductor types and selection criteria.
Cable insulation: As per API RP11S5, cable insulation isolates the electrical potential between conductors and other conducting materials. Insulation also minimizes leakage current from the conductors. Refer to the article ” Cable Insulation ” for more details related to cable insulation classes, advantages and limitations of each class.
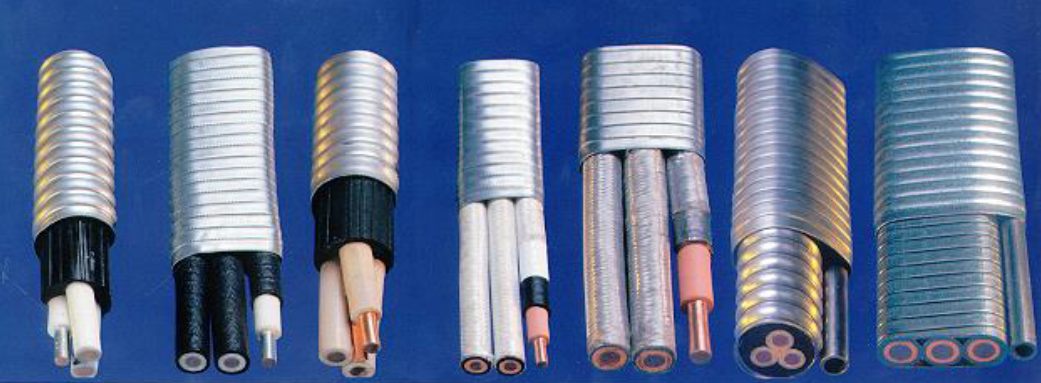
Cable jackets: As per API RP11S5, cable jackets are protective coverings used to mechanically shield the insulation from the downhole environment. The jacket materials protect the insulation from mechanical abuse associated with handling. Refer to the article ” Cable Jackets ” for more details related to cable jacket types and selection criteria.
Braids and coverings: As per API RP11 S5, supplementary layers of materials, named: braids and coverings, are used to guarantee a specific mechanical performance characteristics. It could be either applied over the insulation or on both sides of the jacket. Refer to the article ” Braids and Coverings ” for more details related to braids and coverings types and selection criteria.
Cable armor: As per API RP11S5, cable armor is the outer covering of the cable which provides mechanical protection during installation and removal of cables. In addition to mechanical protection, the armor provides mechanical constraint against swelling and expansion of underlying elastomeric materials in case of any exposure to well fluids. Refer to the article ” Cable Armor ” for more details related to armor profile types and metallurgy selection criteria.
Cable is available in a range of conductor sizes, insulation types and construction to accommodate well conditions, temperatures, etc. The cable manufacturer should be consulted for specific recommendations when adverse well conditions exist.
The economic considerations are governed by power cost, physical dimensions between the tubing and well casing, and the cost of the cable.
Maximum Current Amperage per cable size:
The generally accepted maximum current amperes are as follows:
- AWG No.1 Cu has a capacity of 110 amperes maximum.
- AWG No.2 Cu has a capacity of 94 amperes maximum.
- AWO No.4 Cu has a capacity of 70 amperes maximum.
- AWG No.6 Cu has a capacity of 53 amperes maximum.
You May Also Like…