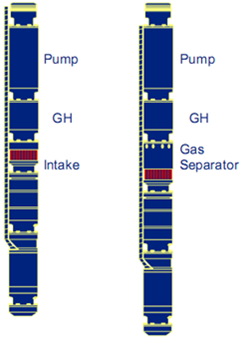
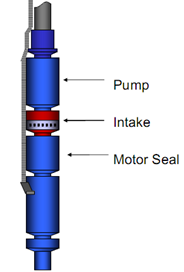
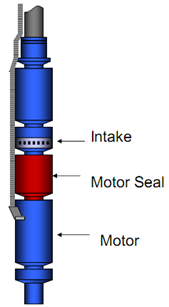
The Motor seal is installed below the intake and above the electric motor. It is also named: Equalizer, balance chamber, or Protector. Seal section types, functions, components, and applications are detailed in this article.
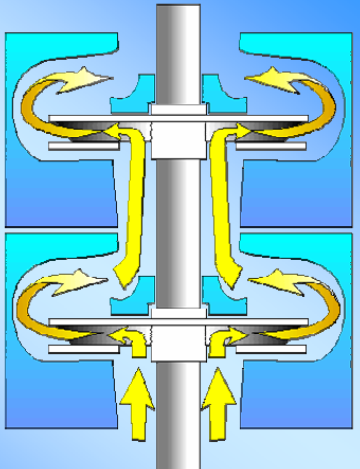
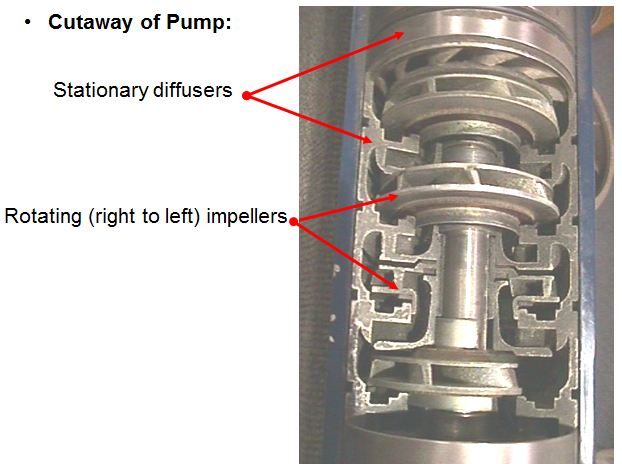
In addition to the main function of transferring the motor torque to the pump shaft, the seal section performs four primary functions (Equalization, Expansion, Isolation, & “Aabsorbsion”):
- Equalizes the pressure in the wellbore with the pressure inside the motor,
- Provides area for motor oil expansion volume (induced by temperature changes in the motor),
- Isolates the well fluid from the clean motor oil,
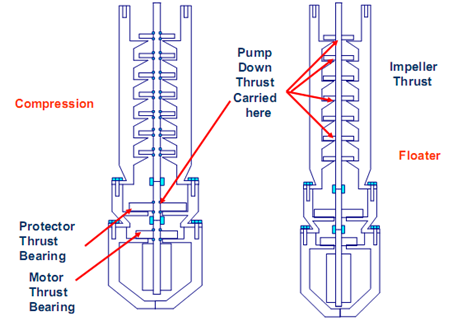
- Absorbs the pump shaft thrust load (it houses the thrust bearing that carries the axial thrust developed by the pump, it can either be upthrust or downthrust, depending on the pumping conditions – obviously, for fixed impeller type only).
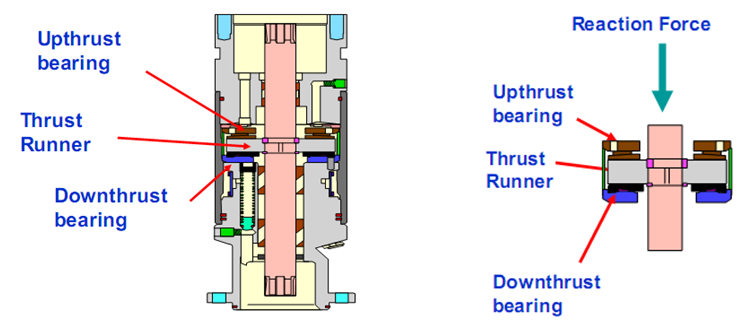
PS: The motor, pump and seal are often submerged below several thousand feet of fluid. The seal section allows the pressure in the motor and the annulus to equalize, so that there is very little pressure across the shaft seals or the pothead connection.
PS: When selecting the protector, we need to be certain that the protector shaft is capable of delivering the full torque required without exceeding its yield strength which could result in a broken shaft.