This article will present the typical ranges of jet pump operating parameters and discusses the advantages and disadvantages of jet pumps in oil wells applications.
Jet Pump Operating Envelope:
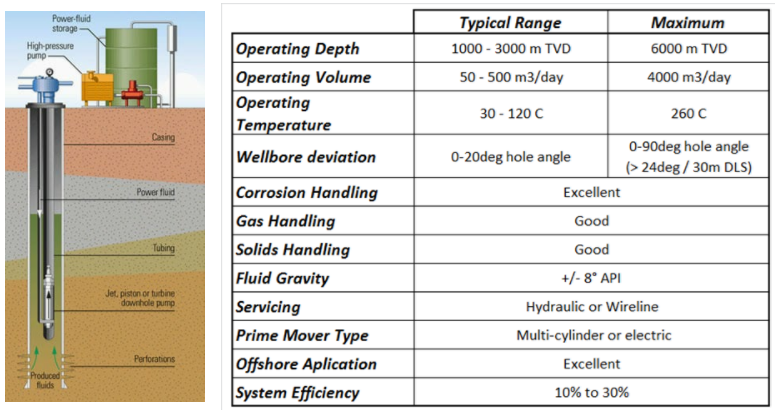
Advantages and disadvantages of jet pumps:
- Advantages:
Jet pumps have several advantages such as:
- no moving parts or mechanical parts that wear.
- Long run life. Providing that erosion is not a major problem, then a working life of at least four years is not unreasonable.
- Capable of high production rates.
- Adjustable to varying production rates by adjusting the power fluid injection rate.
- Low maintenance costs and are easily and quickly retrieved and replaced when maintenance is required.
- The ability to operate for extended periods of time without the need for intervention.
- Power fluid can be sent down the tubing with returns up the annulus (standard circulation) or the power fluid can be sent down the annulus with returns up the tubing (reverse circulation).
- Suitable for low gravity, high pour point crude oils or for controlling paraffin by using reverse circulation with hot water for the power fluid. Chemicals can also be entrained in the power fluid as needed.
- High tolerance to corrosive fluids by the use of CRA materials and/or inhibitors entrained in the power fluid.
- High tolerance to abrasives in the produced fluid.
- Can be used in wells with high deviation angles without causing damage to the tubing.
- Capable of handling high GLR’s.
- The benefits of being able to circulate the downhole pump in and out of the well include reduced downtime and the ability to operate without a pulling unit for tubing, cable, or rod removal.
- Can also be installed in sliding sleeves and nipples using wireline.
- Can also be installed across gas lift mandrels using tubing pack-offs and tubing stops.
- Gages can be installed above and below the jet pump to measure the intake and discharge pressures of the pump, which allows customizing the output of the computer program for a given well.
- Suitable for remote operations.
- Multiple jet pumped wells can be powered by a central surface pump package.
- Disadvantages and limitations:
The disadvantages are:
- Lower efficiencies than other forms of artificial lift resulting in higher horsepower requirements for the power fluid pump (typically the injection rates must be increased due to compensate for the working pressure limits of the system such as the wellhead).
- Power fluid injection rates are typically twice the production rate.
- Space limitations, especially for offshore installations.
- The higher injection rates for the power fluid sometimes result in a higher surface facility investment for handling the volume of fluids returning from the well.
- Backpressure has a pronounced effect on surface injection pressure requirements that varies from approximately 1-1/2 to 1 to approximately 4-1/2 to 1 depending on the area ratio being used.
- High-Pressure Surface Lines
- A jet pump cannot “pump-off” a well. A submergence of approximately 10%, based on the TVD of the location of the jet pump, may be required in order to prevent the problem known as “power fluid cavitation”, which occurs due to the decline in pump-intake-pressure as the well is “pumped-off”.
- A tubing subsurface safety valve is typically employed in any well able to naturally flow to the surface. On some wells, there is also an annular subsurface safety valve. Since there is communication across the jet pump (annulus to tubing and vice versa), then any such safety devices need to be set below the pump in the well. Given that the jet pump is typically set as low (deep) as possible in the well, this creates problems for effective subsurface safety valve deployment.
Reference:
This paper was presented at the 12th Offshore Mediterranean Conference and Exhibition in Ravenna, Italy, March 25-27, 2015.





