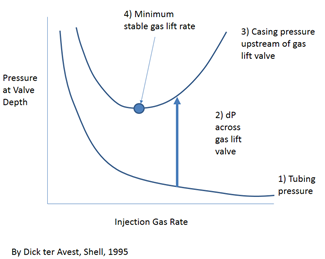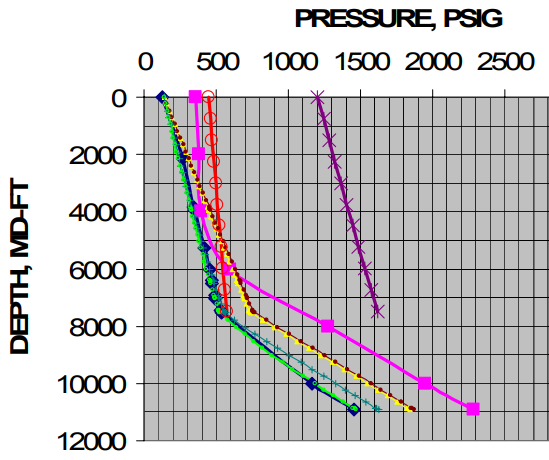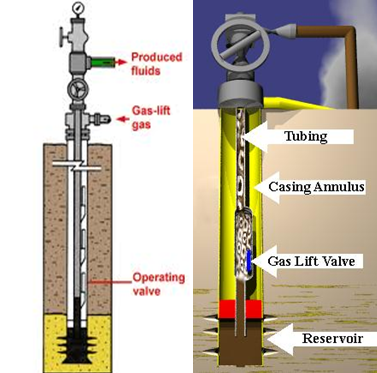
The operation of ”rocking” a gas-lift well, also called: ”fluid level depressing”, is required to unload the well when the fluid column is heavier than the available lift pressure. Thus, the top gas lift valve cannot be uncovered with the available injection-gas pressure.
”Rocking” the well consists on applying an injection gas pressure simultaneously to the tubing and casing. The injected gas in the tubing will push the fluid column back into the formation; therefore reduce height, thus the weight of the fluids being lifted and allow unloading with the available lift pressure.
The tubing pressure is released rapidly, and the source of the major portion of the fluid entering the tubing is load fluid from the annulus. This procedure may be required several times to lower the fluid level in the casing annulus below the depth of the top gas lift valve.
PS: Several hours may be required to ”rock” a well having low reservoir permeability.