Junction box, Check and Drain Valves, Downhole Sensor and Centralizers are some kinds of ESP Accessory Equipment. These type of equipment could play an important role to operate the ESP efficiently and maximize it run lifetime.
Junction Box:
The power cable coming from the well is connected to a surface electric cable leading to the switchboard. As seen in the figure below, the two cables are joined in the junction box, also called a “vent box”. The surface cable connects the junction box to the motor control panel and the motor control panel to the secondary side of the transformers.
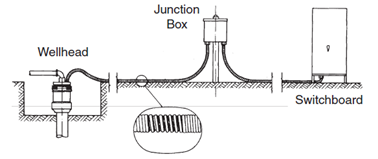
It is a ventilated, weatherproof box performing the following three important functions:
- Provides the electrical connection between the downhole and the surface electric cable.
- Vents any gas to the atmosphere which might reach this point due to migration of well gases up the ESP power cable. The venting of gas eliminates the danger of fire or explosion that could happen if gases travel in the cable to the switchboard.
- Acts as an easily accessible test point for electric checks of the downhole equipment.
Check and Drain Valves:
A check valve is installed about two to three joints above the ESP pump to keep the tubing full liquid when the pump is off. So that, it eliminates the time it takes to raise the fluid from its static fluid level to the surface. In addition, it eliminates the protective shutdown time for fluid fallback.
If the check valve is not installed, the pump should not be started until the fluid column has had a chance to equalize, eliminating the chance for a twisted shaft in the pump, or a burned cable or motor. (A minimum of thirty minutes is recommended.)

When a check valve is used, it is recommended to install a drain valve. The drain valve is generally installed one joint above the check valve. The drain valve has a small drain plug in it, and dropping a bar inside the tubing string will break it and allow the tubing to drain.
NB: In cases of high GOR wells where gas locking is a possibility, the check valve has to be installed higher than normally, about five to six tubing joints above the ESP pump. Actually, when the ESP shuts down, a gas cap can form under the check valve and be held there by the fluid column above the check valve. If the gas cap volume is large enough to extend down to or below the pump intake, the pump will be immediately gas locked and unable to pump fluids.
Downhole sensor:
Downhole sensors are generally attached to the bottom of the motor. These sensors monitor the well pressure and temperature. In some types of downhole sensors, other parameters could be monitored (such as flow, motor temperature, pump discharge pressure, oil dielectric strength and vibration). The information is sent up the power cable to a surface readout in the motor controller.
The down-hole data acquisition instrument can be very helpful in providing important production information. It can be used for the daily monitoring, production optimization, anomalies detection and troubleshooting.
Centralizer:
Centralizers are used to center the motor, pump, and cable during installation. It is recommended to use centralizes in deviated wells to allow proper cooling by keeping the motor centered. Furthermore, centralizers are used to protect corrosion coatings during installation (prevent tubing/downhole equipment friction). When centralizers are used, care should be taken to insure that the centralizers will not rotate.






