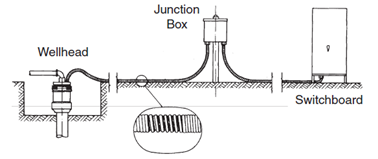
The ESP submersible pumping system consists of both downhole and surface components. The surface components are transformers, motor controllers, junction box and wellhead.
The wellhead accommodates the passage of the power cable from the surface to the wellbore.
The main down-hole components are the motor, seal, pump, and cable. Additional accessory equipment may include the gas separators, check and drain valves, cable bands and protectors, and downhole sensors.
Technologies, types, recommended practices and selection criteria of each compound of the ESP pumping system are discussed in the following list of 22 posts.