Baker Hughes Centrilift AutographPC ™ is an artificial lift and application simulation software. It’s a powerful tool to give a comprehensive and user-friendly system design. This software can be used to design production systems, including: electrical submersible pumping (ESP) systems; electrical submersible progressing cavity pumping (ESPCP™) systems; rod-driven progressing cavity pumping (RDPCP™) systems; horizontal surface pumping (HPump™) systems; and gas lift systems, etc.
Each system installation is unique and with this software, all the well information, including production characteristics, fluid properties and well conditions, can be entered during the initial design phase to produce the optimum solution for each sizing.
Once installed and launched, Design Modes Screen, shown in the following screenshot, appears. Design Modes screen has been added to AutographPC since July 12, 2017. This is the screen where the user can select a design mode and start a new sizing program.
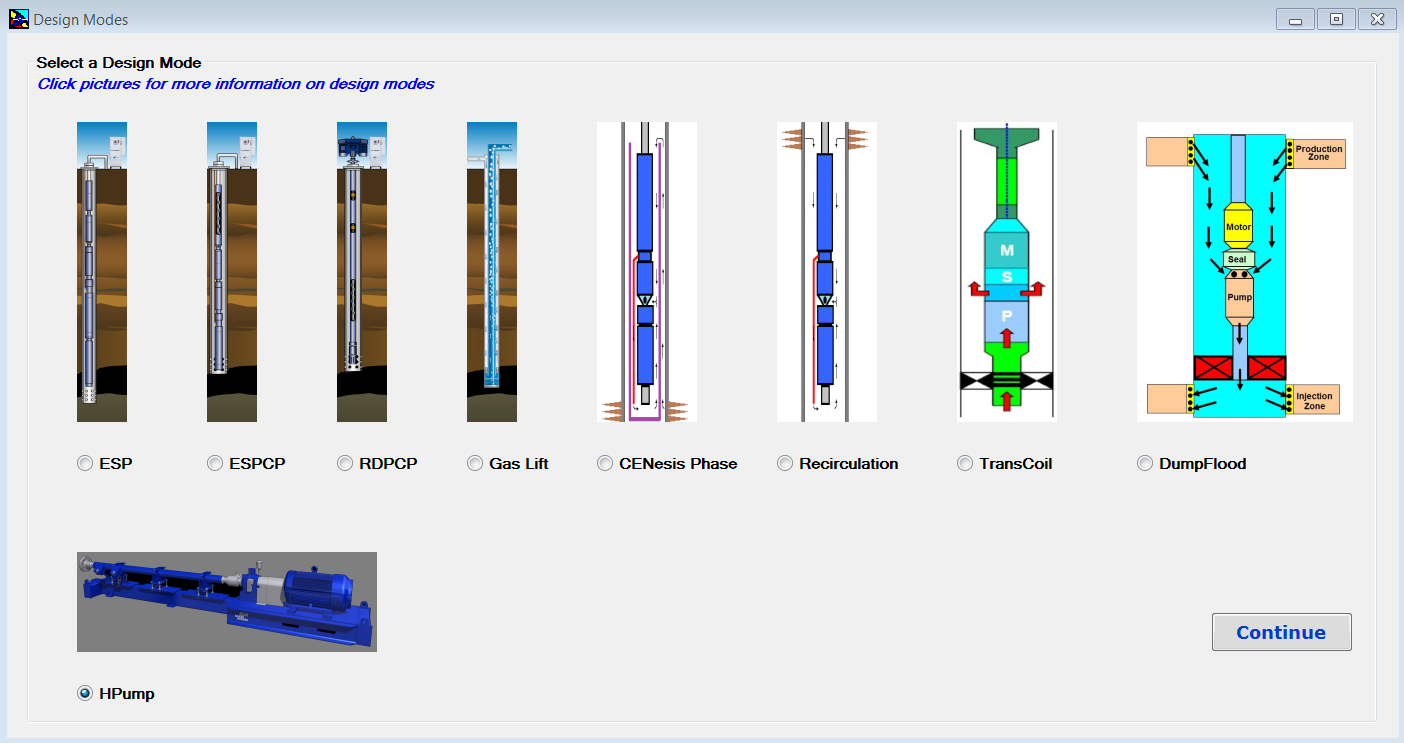
Continue reading →